Delivering Sustainability
The health of all animals is inextricably linked to the wellbeing of people and planet. Healthier animals need fewer natural resources, allowing them to provide more food, labor, fertilizer, companionship, and assistance for less feed, water, and land. Their contribution is central to efforts toward achieving the United Nation’s Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs) by 2030.
Innovations on the horizon in animal health can reduce the threat of disease thanks to stronger immunity, improved prevention strategies, earlier and more specific diagnosis, and more accurate and effective treatment. Bringing these innovations to fruition means lower emissions, reduced natural resource use, and fewer animals lost. Yet for all the promise of growing veterinary knowledge and expertise, it is taking animal health companies increasingly longer and becoming more expensive to bring new products to market.
Sustainable Benefits of New Vaccines
More effective vaccines and delivery mechanisms can help protect more animals against diseases, which means:
- Protecting the livelihoods of the millions worldwide who rely on livestock (SDG 1, 8 and 10)
- Reducing the need for antibiotics, which minimizes the risk of antimicrobial resistance and helps protect public and environmental health (SDG 3, 15)
- Reducing the risk of zoonotic diseases passing from animals to people by preventing them in animals in the first place (SDG 3)
Sustainable Benefits of Alternatives to Antibiotics
Developing new products that prevent or treat bacterial infection while reducing the burden on antibiotics offers benefits for animal health and wellbeing, as well as:
- Improving efficiencies in animal agriculture, which generates greater income for farmers (SDG 1 and 8) and produces more food for the global supply chain (SDG2)
- Reducing the risk of antimicrobial resistance, which strengthens global public health (SDG3)
- Reducing the potential impact of antibiotic use on the environment (SDG12)
Sustainable Benefits of Digital Technologies
Early detection of diseases and individually targeted treatments can bring several benefits for animal health and help support sustainable development, for instance:
- Reducing costs associated with sick animals and supporting agricultural productivity around the world (SDG 1, 2 and 8)
- Optimizing the use of labor and creating new opportunities for agricultural workers and youth (SDG 1 and 8)
- Improving the accuracy of diagnostics and treatments, thereby reducing the need for antibiotics and helping protect public health (SDG 3)
Sustainable Benefits of Diagnostics
Improved diagnostics – remote as well as on-site – will help protect animals against severe disease, which also means:
- Safeguarding the livelihoods of millions of people who rely on livestock (SDG 1, 2 and 8)
- Reducing the use of antibiotics and thus helping minimize potential antimicrobial resistance – a major threat to public health (SDG 3)
- Limiting the transmission of zoonotic diseases that spread between animals and humans (SDG 3)
Sustainable Benefits of Parasite Control
New methods for parasite control can help improve animal health and manage resistance to existing technologies, which can deliver sustainability improvements such as:
- Greater productivity as a result of improved health (SDG1, 2 and 8)
- Reducing the potential impact of parasiticide use on the environment (SDG 12)
Sustainable Benefits of Nutrition
Improving animal health through precision nutrition, feed additives, and biological parasiticides offers multiple benefits to animal health and wellbeing, as well as greater sustainability, such as:
- Greater productivity as a result of improved health (SDG1, 2 and 8)
- Increased levels of traceability for consumers (SDG12)
- Fewer resources needed and lower emissions (SDG13 and 15)
Sustainable Benefits of Safe Development
Developing ways to test new drugs or treatments that require fewer animals can protect animal welfare, and make product research and development safer and more sustainable through:
- Developing treatments faster and with more precision to protect agricultural livelihoods (SDG1 and 8)
- Sharing knowledge of biomarkers across human and animal health (SDG3)
- Reducing the cost and losses of live animals (SDG12 and 15)
Industry Snapshot
Who we are and what we do
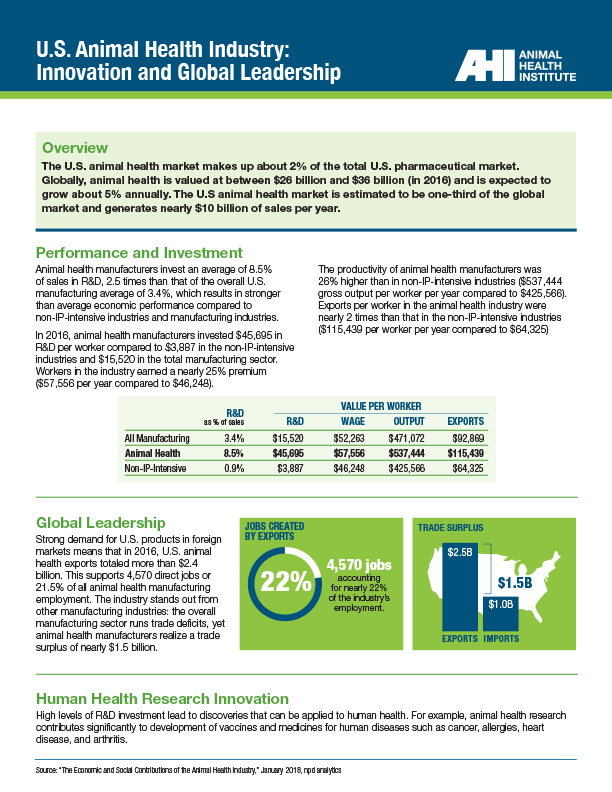
The U.S. animal health market makes up about 2% of the total U.S. pharmaceutical market ($9.9 billion animal compared to $450 billion human medicines). About 60% of animal health sales in the U.S. are companion animal products and about 40% are food-producing animal products.
Pharmaceuticals account for more than half of sales, flea and tick medications are about 29% of the industry, and biologics are just over 19% of the industry.
The U.S. animal health market is estimated to be one-third of the global market and generates around $10 billion of sales per year.
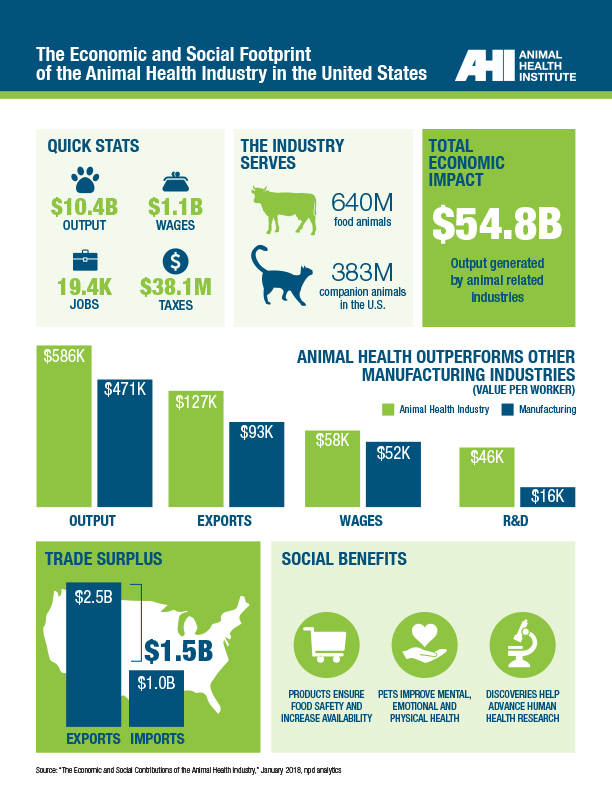
Economic Contributions of the Animal Health Industry
Direct and indirect economic impact
The animal health industry contributes directly to the U.S. economy through jobs, wages, exports, and taxes. Animal health products also support and enable other industries and enhance the quality of life for millions of Americans.
In 2016, animal health companies produced $11.4 billion of medicines in the U.S., of which nearly $9.0 billion was sold domestically and $2.4 billion was exported. The economic impact of the industry plus the industries that depend on animal health – veterinary services, pet services, and meat and dairy production – generated about $560 billion in output and created nearly 1.4 million jobs that paid $53.2 billion in wages in 2016.
Industry Leadership and Innovation
R&D, global outlook, and contributions to innovation
Animal health manufacturers invest an average of 8.5% of sales in R&D, 2.5 times that of the overall U.S. manufacturing average of 3.4%. Strong demand for U.S. products in foreign markets means that in 2016, U.S. animal health exports totaled more than $2.4 billion.
High levels of R&D investment lead to discoveries that can be applied to human health: animal health research contributes to development of vaccines and medicines for human diseases such as cancer, allergies, heart disease, and arthritis.
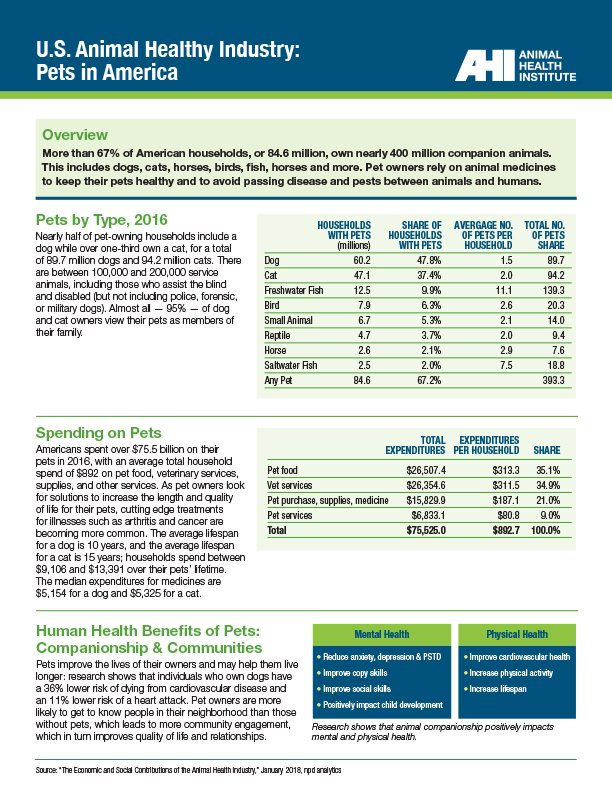
Pets in America
More than 67% of American households own pets, totaling nearly 400 million pets, including dogs, cats, horses, birds, fish, horses and more.
Americans spent over $75.5 billion on their pets in 2016, with an average total household spend of $892 on pet food, veterinary services, supplies, and other services. The median lifetime expenditures for medicines are $5,154 for a dog and $5,325 for a cat. We love our pets!
Pets improve their owners’ overall health and wellbeing and may help them live longer: research shows dog owners have a 36% lower risk of dying from cardiovascular disease and an 11% lower risk of a heart attack.
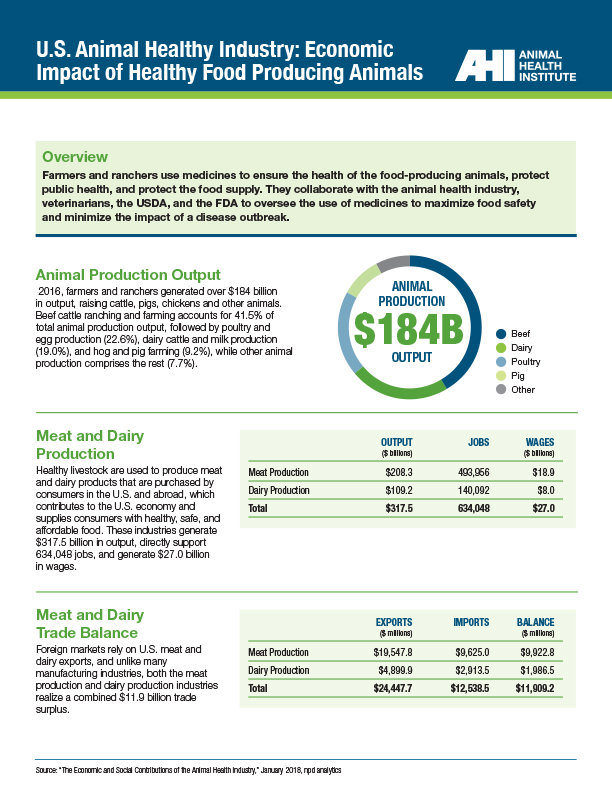
Food-Producing Animals
Healthy livestock means safe and affordable food
Farmers and ranchers use medicines to ensure the health of food-producing animals, protect public health, and protect the food supply.
In 2016, farmers and ranchers generated over $184 billion in output, raising cattle, pigs, chickens and other animals. Healthy livestock are used to produce meat and dairy products purchased by consumers in the U.S. and abroad, which contributes to the U.S. economy and supplies consumers with healthy, safe, and affordable food. Research shows healthy animals carry fewer pathogens that can cause disease in people.